Vitamin D Toxicity Is Associated With
Vitamin D has 2 main forms:
-
D2 (ergocalciferol)
-
D3 (cholecalciferol): The naturally occurring form and the form used for low-dose supplementation
Vitamin D3 is synthesized in skin by exposure to direct sunlight (ultraviolet B radiation) and obtained in the diet chiefly in fish liver oils and salt water fish (see table Sources, Functions, and Effects of Vitamins Sources, Functions, and Effects of Vitamins Vitamins may be Fat soluble (vitamins A, D, E, and K) Water soluble (B vitamins and vitamin C) The B vitamins include biotin, folate, niacin, pantothenic acid, riboflavin (B2), thiamin (B1)... read more ). In some developed countries, milk and other foods are fortified with vitamin D. Human breast milk is low in vitamin D, containing an average of only 10% of the amount in fortified cow's milk.
Vitamin D levels may decrease with age because skin synthesis declines. Sunscreen use and dark skin pigmentation also reduce skin synthesis of vitamin D.
Vitamin D is a prohormone with several active metabolites that act as hormones. Vitamin D is metabolized by the liver to 25(OH)D (calcifediol, calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D), which is then converted by the kidneys to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, calcitriol, or active vitamin D hormone). 25(OH)D, the major circulating form, has some metabolic activity, but 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is the most metabolically active. The conversion to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is regulated by its own concentration, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and serum concentrations of calcium and phosphate.
Vitamin D and related analogs may be used to treat psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease that manifests most commonly as well-circumscribed, erythematous papules and plaques covered with silvery scales. Multiple factors contribute, including... read more 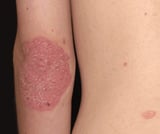 , hypoparathyroidism, and renal osteodystrophy Calcium and phosphate Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is long-standing, progressive deterioration of renal function. Symptoms develop slowly and in advanced stages include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, dysgeusia... read more
, hypoparathyroidism, and renal osteodystrophy Calcium and phosphate Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is long-standing, progressive deterioration of renal function. Symptoms develop slowly and in advanced stages include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, dysgeusia... read more  . Vitamin D's usefulness in preventing leukemia and breast, prostate, colon, or other cancers has not been proved, nor has its efficacy in treating various other nonskeletal disorders in adults (1–3 General references Inadequate exposure to sunlight predisposes to vitamin D deficiency. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, causing rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults and possibly contributing... read more ). Vitamin D supplementation does not effectively treat or prevent depression or cardiovascular disease (4, 5 General references Usually, vitamin D toxicity results from taking excessive amounts. In vitamin D toxicity, resorption of bone and intestinal absorption of calcium is increased, resulting in hypercalcemia. Marked... read more ), nor does it prevent fractures or falls. Some evidence, however, suggests that taking the combined recommended daily allowance of both vitamin D and calcium reduces the risk of hip fractures (6 General references Inadequate exposure to sunlight predisposes to vitamin D deficiency. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, causing rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults and possibly contributing... read more ).
. Vitamin D's usefulness in preventing leukemia and breast, prostate, colon, or other cancers has not been proved, nor has its efficacy in treating various other nonskeletal disorders in adults (1–3 General references Inadequate exposure to sunlight predisposes to vitamin D deficiency. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, causing rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults and possibly contributing... read more ). Vitamin D supplementation does not effectively treat or prevent depression or cardiovascular disease (4, 5 General references Usually, vitamin D toxicity results from taking excessive amounts. In vitamin D toxicity, resorption of bone and intestinal absorption of calcium is increased, resulting in hypercalcemia. Marked... read more ), nor does it prevent fractures or falls. Some evidence, however, suggests that taking the combined recommended daily allowance of both vitamin D and calcium reduces the risk of hip fractures (6 General references Inadequate exposure to sunlight predisposes to vitamin D deficiency. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, causing rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults and possibly contributing... read more ).
![]()
-
1. Autier P, Mullie P, Macacu A, et al: Effect of vitamin D supplementation on non-skeletal disorders: A systematic review of meta-analyses and randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 5 (12):986–1004, 2017. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30357-1
-
2. Manson JE, Cook NR, Lee IM, et al: Vitamin D supplements and prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 380(1):33-44, 2019. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809944
-
3. LeFevre ML, LeFevre NM: Vitamin D screening and supplementation in community-dwelling adults: Common questions and answers. Am Fam Physician 97(4):254-260, 2018.
-
4. Okereke OI, Reynolds CF 3rd, Mischoulon D, et al: Effect of long-term vitamin D3 supplementation vs placebo on risk of depression or clinically relevant depressive symptoms and on change in mood scores: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(5):471-480, 2020. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.10224
-
5. Barbarawi M, Kheiri B, Zayed Y, et al: Vitamin D supplementation and cardiovascular disease risks in more than 83,000 individuals in 21 randomized clinical trials: A meta-analysis [published correction appears in JAMA Cardiol 2019 Nov 6]. JAMA Cardiol 4(8):765-776, 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.1870
-
6. Yao P, Bennett D, Mafham M, et al: Vitamin D and calcium for the prevention of fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2(12):e1917789, 20019. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17789
Symptoms and Signs of Vitamin D Toxicity
The main symptoms of vitamin D toxicity result from hypercalcemia Hypercalcemia Hypercalcemia is a total serum calcium concentration > 10.4 mg/dL (> 2.60 mmol/L) or ionized serum calcium > 5.2 mg/dL (> 1.30 mmol/L). Principal causes include hyperparathyroidism, vitamin... read more . Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting can develop, often followed by polyuria, polydipsia, weakness, nervousness, pruritus, and eventually renal failure. Proteinuria, urinary casts, azotemia, and metastatic calcifications (particularly in the kidneys) can develop.
-
Hypercalcemia plus risk factors or elevated serum 25(OH)D levels
A history of excessive vitamin D intake may be the only clue differentiating vitamin D toxicity from other causes of hypercalcemia. Elevated serum calcium levels of 12 to 16 mg/dL (3 to 4 mmol/L) are a constant finding when toxic symptoms occur. Serum 25(OH)D levels are usually elevated to > 150 ng/mL (> 375 nmol/L). Levels of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, which need not be measured to confirm the diagnosis, may be normal.
Serum calcium should be measured often (weekly at first, then monthly) in all patients receiving large doses of vitamin D, particularly the potent 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D.
-
IV hydration plus corticosteroids or bisphosphonates
After stopping vitamin D intake, hydration (with IV normal saline) and corticosteroids or bisphosphonates (which inhibit bone resorption) are used to reduce blood calcium levels.
Kidney damage or metastatic calcifications, if present, may be irreversible.
Vitamin D Toxicity Is Associated With
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-gb/professional/nutritional-disorders/vitamin-deficiency-dependency-and-toxicity/vitamin-d-toxicity

Posting Komentar